Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are no longer a luxury for manufacturing companies—they are a necessity. ERP software in manufacturing industries can combine different business processes into a single system. This allows companies to create new ideas, save money, and improve overall efficiency. As manufacturers deal with the problems of modern supply chains, global competition, and quickly changing market demands, ERP systems offer a strategic advantage that’s essential.
Why your manufacturing business needs ERP to innovate
The manufacturing industry has always been at the forefront of technological innovation. From the introduction of assembly lines to the adoption of automation, manufacturers have continuously sought ways to improve efficiency and reduce costs. However, the challenges faced by manufacturers today are more complex than ever before. Globalization, increased competition, and the rise of the digital economy have created an environment where agility and innovation are critical to success.
ERP in manufacturing industries offers a comprehensive ERP software solution to these challenges by providing a centralized platform that integrates various business processes. This integration allows manufacturers to streamline operations, reduce inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions that drive innovation.
1. Integration of business processes: One of the most significant benefits of ERP in manufacturing industries is the integration of various business processes into a single, cohesive system. This integration allows for seamless communication and collaboration across departments, enabling manufacturers to operate more efficiently.
For example, an ERP system can combine production planning, inventory management, and purchasing processes. This makes sure that all parts of the manufacturing process are in line. This integration reduces the likelihood of errors, minimizes delays, and ensures that resources are used efficiently. As a result, manufacturers can focus on innovation and growth, rather than being bogged down by operational inefficiencies.
2. Real-Time data and analytics: In today’s fast-paced business environment, access to real-time data is crucial. ERP in manufacturing industries provides manufacturers with real-time visibility into their operations, allowing them to make informed decisions quickly. This real-time data can be used to monitor production processes, track inventory levels, and analyze market trends.
For instance, a manufacturer can use real-time data from an ERP system to identify bottlenecks in the production process and make adjustments to improve efficiency. Additionally, real-time analytics can help manufacturers forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and reduce the risk of stockouts or overproduction. By leveraging real-time data, manufacturers can stay ahead of the competition and respond quickly to changing market conditions.
3. Automation of repetitive tasks: Manufacturing processes often involve repetitive tasks that can be time-consuming and prone to errors. ERP in manufacturing industries can automate many of these tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic activities.
For example, an ERP system can automate the procurement process by automatically generating purchase orders when inventory levels reach a certain threshold. This automation reduces the likelihood of errors, speeds up the procurement process, and ensures that delays in obtaining materials do not disrupt production schedules.
Additionally, ERP systems can automate tasks such as quality control, production scheduling, and order processing. This automation not only improves efficiency but also ensures that manufacturing processes are consistent and meet high-quality standards.
4. Fostering a culture of continuous improvement: Innovation is not a one-time event—it is an ongoing process. ERP in manufacturing industries supports a culture of continuous improvement by providing the tools needed to monitor performance, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes.
For example, an ERP system can track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production efficiency, scrap rates, and on-time delivery rates. By monitoring these KPIs, manufacturers can identify trends, uncover inefficiencies, and implement changes to improve performance. Additionally, ERP systems can provide insights into customer feedback and market trends, allowing manufacturers to adapt their products and processes to meet changing demands.
Enterprise resource planning as a catalyst for innovation
Innovation is the lifeblood of the manufacturing industry. Companies that fail to innovate risk falling behind their competitors and losing market share. Modern Manufacturing ERP systemis very important for fostering new ideas. It gives the tools and information needed to keep improving and create new products and processes.
1. Streamlining product development processes: One of the key benefits of ERP in manufacturing industries is its ability to streamline product development processes. ERP systems help manufacturers make new products faster by giving them a central place to manage everything from research and development (R&D) to production.
For example, an ERP system can combine research and development, design, and engineering processes. This makes sure that all departments are working together to reach a common goal. This integration reduces the likelihood of errors, minimizes delays, and ensures that new products are developed efficiently.
ERP systems can also show the current state of product development projects. This lets manufacturers watch progress, find problems, and make changes as needed. This visibility is crucial for ensuring that new products are brought to market on time and within budget.

2. Supporting mass customization: In today’s market, consumers are increasingly demanding products that are tailored to their specific needs and preferences. ERP in manufacturing industries supports mass customization by providing the tools needed to produce customized products at scale.
For example, an ERP system can manage the production of special products by automatically making production plans, tracking stock levels, and working with suppliers. This automation allows manufacturers to produce customized products efficiently and cost-effectively, without sacrificing quality.
Furthermore, ERP sysERP systems can also tell you what customers like and what the market is doing. This helps manufacturers make new products that meet the needs of their customers. insights, manufacturers can stay ahead of the competition and differentiate themselves in the market.
3. Leveraging real-time analytics for innovation: Real-time analytics is a powerful tool for driving innovation in the manufacturing industry. ERP in manufacturing industries provides manufacturers with access to real-time data and analytics, enabling them to make informed decisions and identify new opportunities for innovation.
For example, a manufacturer can use real-time analytics to monitor production processes and identify areas for improvement. By analyzing data on production efficiency, scrap rates, and downtime, manufacturers can identify trends and implement changes to improve performance.
Real-time analytics can also be used to track market trends and customer preferences. This helps manufacturers make new products and change their existing offerings to meet changing needs. By leveraging real-time analytics, manufacturers can stay ahead of the competition and drive continuous innovation.
4. Enhancing collaboration and communication: Collaboration and communication are essential for driving innovation in the manufacturing industry. ERP in manufacturing industries enhances collaboration and communication by providing a centralized platform for managing and sharing information across departments.
For example, an ERP system can help teams work together better. It gives them a shared way to manage projects and track their progress. This collaboration ensures that all departments are working together towards a common goal and that new products are developed efficiently.
Furthermore, ERP systems can enhance communication with suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders by providing real-time visibility into production processes and inventory levels. This visibility allows manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in demand, coordinate with suppliers, and ensure that customer orders are fulfilled on time.
5. Driving continuous improvement through AI and machine learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by providing new tools for driving continuous improvement and innovation. ERP in the manufacturing sector is more and more using AI and machine learning. This helps manufacturers improve processes, save money, and make new products.
For example, AI-powered ERP systems can analyze production data and identify patterns that indicate inefficiencies or potential issues. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, these systems can predict equipment failures, optimize production schedules, and recommend changes to improve performance.
AI-powered ERP systems can also give you information about what customers like and what the market is doing. This helps manufacturers make new products and change their offerings to meet changing needs. By incorporating AI and machine learning into their ERP systems, manufacturers can drive continuous improvement and stay ahead of the competition.

ERP: Your competitive edge in the global market
In today’s global marketplace, manufacturing companies are facing increasing pressure to stay competitive. Globalization, fast technology changes, and changing consumer needs have made it harder for manufacturers to succeed. Manufacturing ERP software provides manufacturers with the tools and insights needed to gain a competitive edge and thrive in this challenging environment.
1. Enhancing production efficiency: Efficiency is a key driver of competitiveness in the manufacturing industry. Companies that can produce goods more quickly and at a lower cost than their competitors are better positioned to capture market share and grow their business. Manufacturing ERP software enhances production efficiency by streamlining processes, reducing waste, and optimizing resource use.
For example, an ERP system can automate production scheduling. This makes sure that resources are used well and that production runs smoothly. Additionally, ERP systems can monitor production processes in real-time, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies that need to be addressed. By enhancing production efficiency, manufacturers can reduce costs, increase output, and improve their overall competitiveness.
2. Reducing operational costs: Cost reduction is another critical factor in maintaining competitiveness in the manufacturing industry. ERP in manufacturing helps manufacturers save money by using the right resources, reducing waste, and managing their supply chain better.
For example, an ERP system can help manufacturers optimize inventory levels by providing real-time visibility into stock levels and demand forecasts. This optimization reduces the risk of overproduction and stockouts, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and that costs are minimized.
Furthermore, ERP systems can streamline procurement processes by automating purchase orders and tracking supplier performance. This automation reduces the likelihood of errors, speeds up the procurement process, and ensures that manufacturers are getting the best value for their money. By reducing operational costs, manufacturers can increase their profit margins and invest in innovation and growth.
3. Improving overall product quality: Product quality is a critical factor in maintaining competitiveness in the manufacturing industry. Companies that produce high-quality products are more likely to retain customers, build brand loyalty, and differentiate themselves from their competitors. ERP in manufacturing helps manufacturers make their products better. It gives them tools to control quality, improve processes, and keep improving.
For example, an ERP system can track quality metrics like how many defects, scraps, and rework costs are made. This gives manufacturers real-time information about product quality. Additionally, ERP systems can automate quality control processes, ensuring that products meet high-quality standards before they are shipped to customers.
ERP systems can also give you information about customer satisfaction, what customers say and what the market is doing. This helps manufacturers find ways to improve their products and make new ones that meet customers’ needs. By improving product quality, manufacturers can build a reputation for excellence and gain a competitive edge in the market.
4. Enhancing supply chain management: Effective supply chain management is essential for maintaining competitiveness in the manufacturing industry. ERP in manufacturing industries enhances supply chain management by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, production processes, and supplier performance.
For example, an ERP system can track stock levels in real time. This makes sure that manufacturers have the right raw materials to meet production needs. Additionally, ERP systems can track supplier performance, providing insights into lead times, delivery accuracy, and quality. This visibility allows manufacturers to coordinate with suppliers, optimize inventory levels, and reduce the risk of production disruptions.
Furthermore, ERP systems can provide real-time data on market trends and customer demand, allowing manufacturers to adjust production schedules and supply chain strategies as needed. By enhancing supply chain management, manufacturers can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and respond quickly to changes in demand.
5. Data-driven decision making: In today’s data-driven world, the ability to make informed decisions quickly is a critical factor in maintaining competitiveness. ERP in manufacturing industries gives manufacturers real-time data and analytics. This lets them make decisions based on data that help grow and innovate.
For example, an ERP system can show how well a manufacturing company is making products, how much inventory they have, and what the market is doing. This helps manufacturers find ways to improve their product quality and make plans for growth. Additionally, ERP systems can provide predictive analytics, helping manufacturers forecast demand, manage risks, and plan for the future.
By leveraging data-driven decision-making, manufacturers can stay ahead of the competition and respond quickly to changing market conditions. This agility is crucial for maintaining competitiveness in a rapidly changing global market.
Insights from our manufacturing white paper
Solutions to navigate challenges and drive digital transformation in the Canadian manufacturing industry
 Download our white paper
Download our white paper
Overcoming challenges with ERP implementation in supply chain management
While the benefits of a manufacturing ERP system in manufacturing industries are clear, implementing an ERP system is not without its challenges. Manufacturers must navigate a range of obstacles, including resistance to change, budget constraints, and integration issues, to successfully implement an ERP system and realize its full potential.
1. Resistance to change: One of the most common challenges associated with ERP implementation is resistance to change. Employees may be hesitant to adopt a new system, particularly if they are accustomed to existing processes and workflows. This resistance can slow down the implementation process and reduce the overall effectiveness of the ERP system.
To overcome resistance to change, manufacturers must engage key stakeholders early in the process and provide comprehensive training and support. By involving employees in the decision-making process and demonstrating the benefits of the ERP system, manufacturers can build buy-in and ensure a smoother transition.
For example, manufacturers can conduct workshops and training sessions to educate employees on the benefits of ERP in manufacturing industries and how it will improve their day-to-day operations. Additionally, providing ongoing support and resources can help employees feel more comfortable with the new system and reduce resistance.

2. Budget constraints: Implementing an ERP system can be a significant financial investment, particularly for small and mid-sized manufacturers. Budget constraints can limit the scope of the implementation and delay the realization of benefits.
To manage budget constraints, manufacturers can adopt a phased implementation approach, starting with the most critical modules and gradually expanding the system over time. This approach allows manufacturers to spread the costs of implementation and reduce the financial burden.
For example, a manufacturer might start by using the main parts of the ERP system, like planning production and managing inventory. Then, they would slowly add more parts, like quality management and control and purchasing, as the budget allows. This phased approach ensures that the manufacturer can realize the benefits of ERP in manufacturing industries without exceeding their budget.
3. Integration with existing systems: Another challenge associated with ERP implementation is integrating the new system with existing tools and processes. Many manufacturers rely on legacy systems that may not be compatible with modern ERP solutions. Integration issues can lead to data silos, process inefficiencies, and increased costs.
To overcome integration challenges, manufacturers should choose an ERP system that is flexible and compatible with their existing systems. Additionally, manufacturers should work with experienced implementation partners who can provide guidance and support throughout the integration process.
For example, manufacturers can conduct a thorough assessment of their existing systems and processes to identify potential integration challenges and develop a plan for addressing them. By choosing an ERP system that supports integration and working with experienced partners, manufacturers can ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of ERP in manufacturing industries.
4. Ensuring data accuracy and consistency: Data accuracy and consistency are critical factors in the success of an ERP implementation. Inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to errors, inefficiencies, no cost savings and reduced effectiveness of the ERP system. Manufacturers must ensure that their data is accurate, up-to-date, and consistent across all departments before implementing an ERP system.
To fix data accuracy and consistency problems, manufacturers should do a thorough data audit before using the system. They should find and fix any differences or inconsistencies. Manufacturers should also set up rules and ways to manage data. These rules should make sure that data is accurate and consistent during the process of using it and after.
For example, manufacturers can set up checks to make sure data is correct and used in the same way in all departments. By ensuring data accuracy and consistency, manufacturers can maximize the effectiveness of ERP in manufacturing industries and realize the full benefits of the system.
5. Managing change and ensuring user adoption: Successful ERP implementation requires effective change management and user adoption. Manufacturers must ensure that employees are fully trained and comfortable with the new system to maximize its effectiveness. Resistance to change and lack of user adoption can hinder the success of an ERP implementation and reduce the return on investment.
To manage change and ensure user adoption, manufacturers should develop a comprehensive change management plan that includes training, communication, and support. This plan should be tailored to the specific needs of the organization and address any concerns or challenges that employees may have.
For example, manufacturers can conduct regular training sessions and provide ongoing support to help employees feel comfortable with the new system. Additionally, manufacturers can establish clear communication channels to address any questions or concerns that employees may have during the implementation process. By effectively managing change and ensuring user adoption, manufacturers can maximize the benefits of ERP in manufacturing industries and achieve a successful implementation.
Popular manufacturing ERP software solutions for manufacturing industries
As more and more companies need manufacturing ERP systems, many solutions have come out to meet the special needs of manufacturers. These manufacturing ERP solutions have many features, from planning production and managing inventory to controlling quality and managing money. Below are some of the most popular ERP solutions for manufacturing industries:
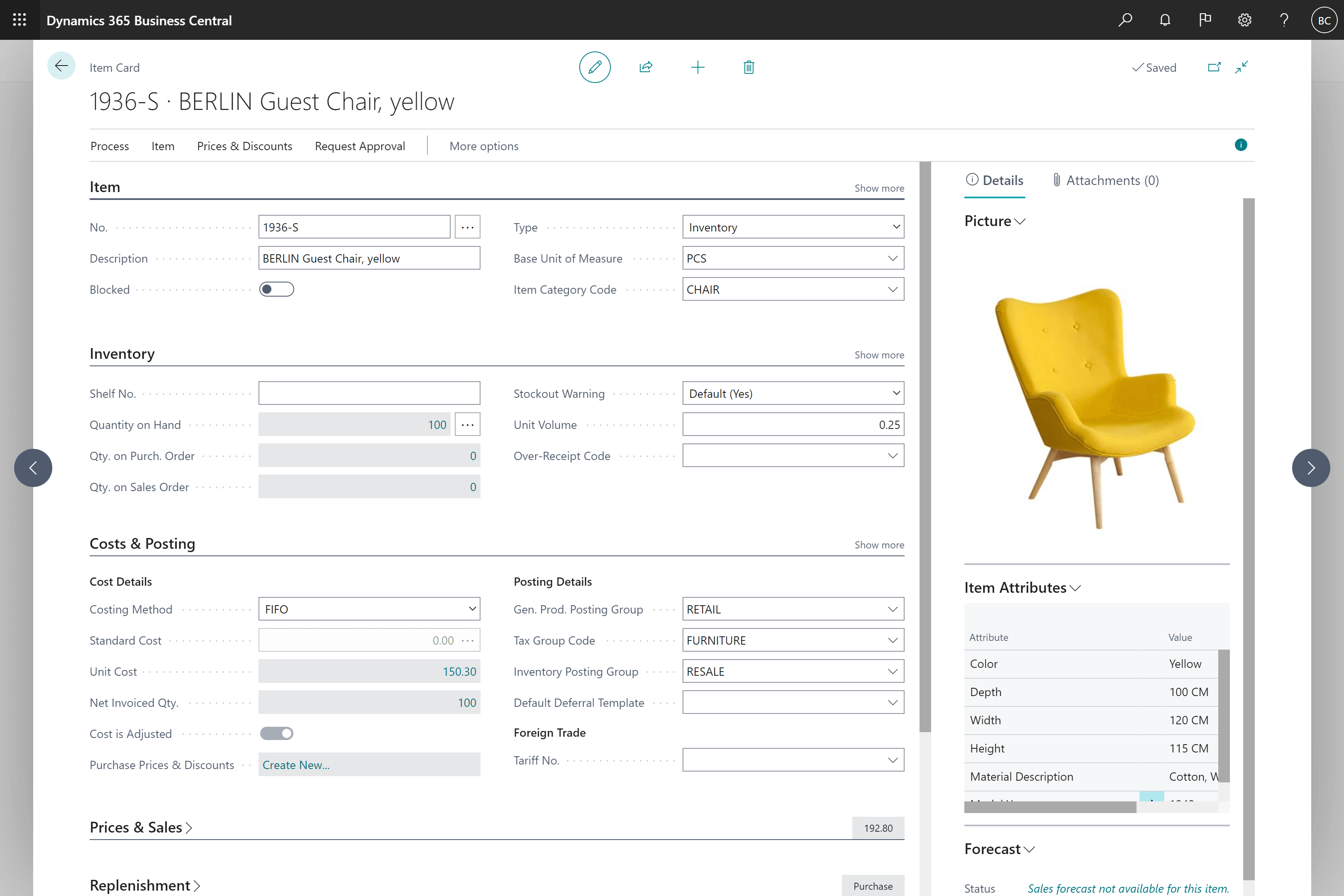
1. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central: Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is a comprehensive ERP solution designed for small to mid-sized manufacturing businesses. It has many features, including planning production, managing inventory, buying things, and customer relationship management managing money, and managing customer relationships.
One of the key strengths of Business Central is its flexibility and scalability. It can be made to fit the needs of different manufacturing industries, whether it’s one-time manufacturing, process manufacturing, or mixed-mode manufacturing. Business Central works well with other Microsoft products, like Office 365 and Power BI. This gives manufacturers a single platform to manage their operations.
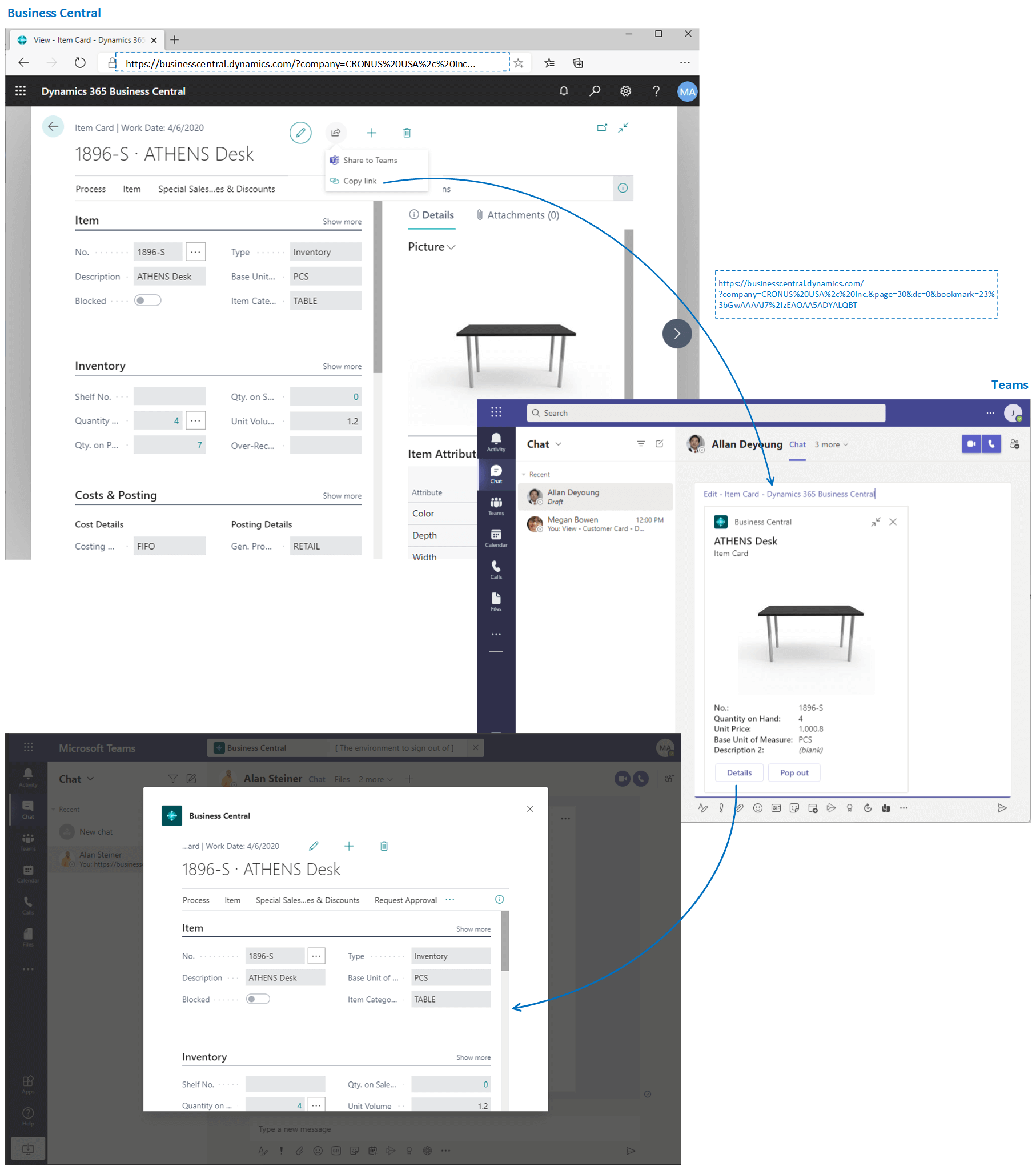
A unique feature of Business Central is Copilot, an AI-powered assistant that acts as an everyday companion for users. Copilot helps automate daily tasks, look at data, and give you predictions. This helps manufacturers make better decisions and improve their operations.

2. SAP S/4HANA: SAP S/4HANA is a leading ERP solution for large manufacturing enterprises. It is known for its powerful analytics and real-time data processing. This makes it a great choice for manufacturers with complex operations and large production processes.
SAP S/4HANA offers a comprehensive suite of modules, including production planning, inventory management, quality control, product lifecycle management, supply chain management, and financial management. The system’s advanced analytics capabilities allow manufacturers to gain deep insights into their operations, identify inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions to improve performance.
One of the key advantages of SAP S/4HANA is its ability to handle large volumes of data in real-time. This real-time data processing lets manufacturers watch production processes, track stock levels, and analyze market trends, all in real time. SAP S/4HANA’s in-memory database technology also makes it easy to find and process data quickly. This helps manufacturers make quick decisions and respond to changing market conditions.
3. Oracle NetSuite: Oracle NetSuite is a cloud-based ERP solution that caters to growing manufacturing businesses. It offers a range of functionalities for manufacturing management, including production management, inventory control, order management, procurement, and financial management. NetSuite is particularly well-suited for manufacturers that require a flexible and scalable ERP solution that can grow with their business.
NetSuite’s cloud-based architecture allows manufacturers to access the system from anywhere, providing real-time visibility into operations and enabling remote collaboration. The system’s built-in analytics and reporting tools allow manufacturers to track key performance metrics, monitor production processes, and make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
NetSuite also offers a range of industry-specific modules, allowing manufacturers to tailor the system to their specific needs. For example, process manufacturers can use NetSuite’s batch management and recipe management features. Discrete manufacturers can use the system’s bill of materials (BOM) and work order management features.
4. Infor CloudSuite Industrial (SyteLine): Infor CloudSuite Industrial (formerly known as SyteLine) is an ERP solution designed specifically for manufacturing industries. It has all the features you need for industrial manufacturing, from planning and scheduling to delivering your products. This makes it a great choice for manufacturers with complex supply chains and production processes.
Infor CloudSuite Industrial provides a comprehensive suite of modules, including production planning, inventory management, procurement, quality control, business management, and financial management. The system’s advanced planning and scheduling (APS) capabilities allow manufacturers to optimize production schedules, minimize lead times, and reduce inventory levels.
One of the key strengths of Infor CloudSuite Industrial is its flexibility and customization options. The system can be made to fit the needs of different manufacturing industries, like aerospace and defense, cars, or food and beverage. Additionally, Infor CloudSuite Industrial’s cloud-based architecture allows manufacturers to access the system from anywhere and scale their operations as needed.
5. Epicor ERP: Epicor ERP is a comprehensive ERP solution designed for manufacturing industries of all sizes. It offers a wide range of functionalities, including production management, inventory control, warehouse management, supply chain management, financial management, and CRM. Epicor ERP is particularly well-suited for manufacturers that require a flexible and scalable ERP solution that can support both discrete and process manufacturing.
Epicor ERP’s advanced production management features let manufacturers manage complex production processes, track work orders, and track how well their products are made. The system’s real-time analytics and reporting tools let manufacturers see how their products are doing, how much they have, and what the market is doing. This helps them make smart decisions based on data and improve efficiency.
Epicor ERP has many parts that can be changed to fit the needs of different companies. This makes it easy for manufacturers to make the system work for them. For example, manufacturers can add modules for their industry, like project management, field service management, or even human resources and capital management. This will make the system fit their needs.
Case study
Discover how Bédard Ressources made its accounting more efficient with Business Central

The future of ERP in manufacturing
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the role of ERP in manufacturing operations. The future of ERP for manufacturing, is likely to be shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), predictive analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies will further enhance the capabilities of ERP systems, enabling manufacturers to achieve even greater levels of efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness.
1. AI integration: AI-powered ERP systems are poised to revolutionize the manufacturing industry by providing new tools for driving continuous improvement and innovation. AI integration in ERP systems allows manufacturers to optimize processes, reduce costs, and develop new products.
For example, AI-powered ERP systems, like Copilot for Business Central, help users do daily tasks. They help them automate routine tasks, improve production schedules, and give helpful suggestions. Copilot enhances day-to-day business operations by offering predictive insights and helping users make more informed decisions, ultimately driving better outcomes in manufacturing.
AI-powered ERP systems can also analyze production data and identify patterns that indicate inefficiencies or potential issues. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, these systems can predict equipment failures, optimize production schedules, and recommend changes to improve performance.
2. IoT integration: The Internet of Things (IoT) is another technology that is transforming the manufacturing industry and enhancing the capabilities of ERP systems. IoT integration in ERP systems allows manufacturers to monitor production processes in real-time, track equipment performance, and gain valuable insights into their operations.
For example, ERP systems that use IoT can get data from sensors and devices on the shop floor. This gives you real-time information about how your company is doing things, what equipment is working well, and how much inventory you have. This real-time data allows manufacturers to identify bottlenecks, optimize production schedules, and reduce downtime.
IoT integration also enables manufacturers to implement predictive maintenance strategies, reducing the risk of equipment failures and minimizing unplanned downtime. By watching how equipment works in real time, manufacturers can find problems before they cause costly breakdowns. This will make sure that production runs smoothly and efficiently.
3. Predictive analytics: Predictive analytics is a powerful tool for using business intelligence, driving innovation and improving decision-making in the manufacturing industry. Predictive analytics capabilities in ERP systems allow manufacturers to forecast trends, manage risks, and plan for the future with greater accuracy.
For example, predictive analytics in ERP systems can analyze historical data on production efficiency, demand patterns, and market trends to forecast future demand and optimize production schedules. This forecasting capability allows manufacturers to adjust their production plans, manage inventory levels, and reduce the risk of stockouts or overproduction.
Predictive analytics can also be used to find possible risks and opportunities in the supply chain. This helps manufacturers to fix problems quickly and take advantage of new opportunities. By leveraging predictive analytics, manufacturers can stay ahead of the competition and drive continuous improvement in their operations.
4. Cloud-based ERP solutions: Cloud-based ERP solutions are becoming increasingly popular in the manufacturing industry due to their flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud-based ERP systems allow manufacturers to access their data and applications from anywhere, providing real-time visibility into operations and enabling remote collaboration.
For example, cloud-based ERP solutions such as Oracle NetSuite and Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central offer a range of features and modules that can be customized to meet the specific needs of different manufacturing industries. These systems use the cloud to let manufacturers grow as needed. They don’t need to spend a lot of money on hardware or infrastructure at first.
Cloud-based ERP solutions also cost less to own than on-premise systems. They do not need to spend a lot of money on hardware, software, and IT resources. Cloud-based ERP systems are usually updated automatically by the vendor. This means that manufacturers always have the latest features and security patches.
5. Enhanced user experience (UX) and mobility: The future of ERP in manufacturing will also be shaped by advancements in user experience (UX) and mobility. Modern ERP systems are increasingly focused on providing intuitive and user-friendly interfaces, as well as mobile access to data and applications.
For example, ERP systems such as SAP S/4HANA and Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central offer mobile apps that allow users to access real-time data, monitor production processes, and make decisions on the go. These mobile features are especially useful for manufacturers with many locations. They let managers and employees stay connected and work together from anywhere.
Additionally, modern ERP systems are increasingly incorporating AI-powered virtual assistants, such as Copilot, to enhance the user experience. These virtual assistants provide users with personalized recommendations, automate routine tasks, and help users navigate the system more efficiently. By improving user experience and mobility, ERP systems are becoming easier to use. This makes them more popular and helps them get better results.
6. Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing: The rise of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing is driving the adoption of advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and big data analytics in the manufacturing industry. ERP systems are important for making smart manufacturing possible. They give a single platform for managing and improving production processes, supply chains, and customer relationships.
Smart manufacturing uses IoT devices, AI-powered analytics, and cloud-based ERP systems to create a connected and data-driven manufacturing environment. ERP systems let manufacturers get and analyze data from sensors and devices on the factory floor. They can also make production schedules better right away, and respond quickly to changes in demand.
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is also driving the development of smart factories, where production processes are automated, and decisions are made based on real-time data. ERP systems are at the heart of these smart factories, providing the tools and insights needed to drive efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness.

Conclusion: Don’t get left behind—leverage ERP to innovate and compete
In the end, ERP in manufacturing is not just a tool for managing business processes. It is a key driver of new ideas, efficiency, and competitiveness in today’s market. By embracing ERP systems, manufacturers can streamline their operations, optimize resource use, reduce costs, and improve product quality. Additionally, ERP systems provide the tools and insights needed to drive continuous improvement, foster innovation, and stay ahead of the competition.
As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, the role of ERP systems will become increasingly important. The use of AI, IoT, predictive analytics, and cloud-based solutions will make ERP systems even better. This will help manufacturers do more efficient, creative, and competitive work.
Now is the time for manufacturers to explore and implement ERP solutions that can propel their business forward. By using ERP in manufacturing, manufacturers can be successful for a long time. They can also make sure they are ready for the challenges and opportunities of the future.
Ready to transform your manufacturing operations with an ERP?
Don’t let outdated processes hold your business back. Contact us today to discover how our tailored ERP in manufacturing industries solutions can help you innovate, streamline your operations, and stay ahead of the competition. Our experts are here to guide you every step of the way. Get in touch with us now to schedule a free consultation and start your journey towards manufacturing excellence with the right ERP system!
 Contact Sales
Contact Sales
Liked what you just read? Sharing is caring.

August 19, 2024 by Arianne Pellerin by Arianne Pellerin Marketing Specialist
Driven by an unwavering obsession to optimize processes and revolutionize marketing with innovative ideas, I never stop searching for the perfect solution. My true passion lies in crafting dreamlike experiences by harnessing the full potential of web analytics and cutting-edge digital strategies. As a blog writer for Gestisoft, I bring this expertise to the forefront, focusing primarily on our ERP solutions.
